17
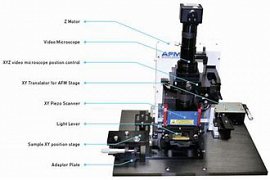
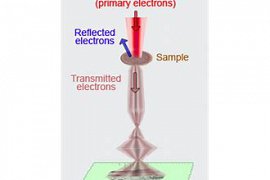
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Electron microscope, transmission or TEM, the kind of the electron microscope is the ability to capture the microstructure of materials with a magnification of 1, The 000 up to 1٬000٬000 equal to the power of separation in the limit of smaller than 1 nm. Microscope, transmission electron as well as the ability elemental Analyzer is to determine the structure and direction of the crystalline components to the small 30 Nm for quantitative and qualitative....